Creating and implementing game-play classes
Unreal Engine use C++ for programming language so when we creating game-play C++ class in engine this is comprised in header file (.h) and a source file (.cpp).
Header file and Source file
- Declarations of the class and its members like variables and functions
- Where the functionality is defined by implementing the function that belong to the class or define in Header file.
Unreal engine uses standardized naming scheme so we find instantly what king of class it is. Looking on first letter of class or prefix;
| Prefix | Meaning |
| A | Actors and Spawned directly into wold |
| U | All game-play objects. These not directly instanced into the world, they belong from actor; Generally objects like Components; |
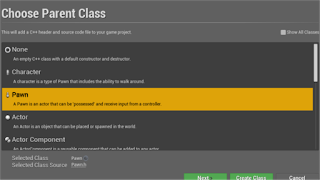
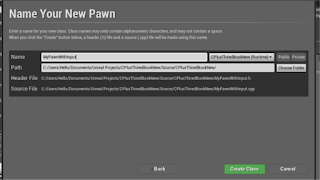
Create new c++ class and explore this;
Class Headers
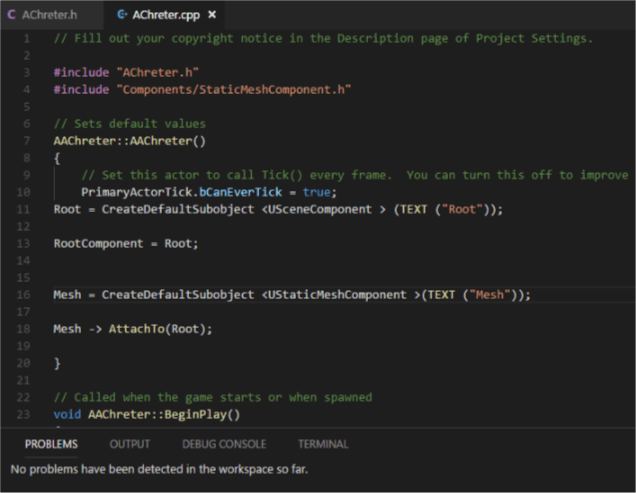
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings.
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "GameFramework/Actor.h"
#include "ES_SpawanEnemy.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class COVERTRACK_API AES_SpawanEnemy : public AActor
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this actor's properties
AES_SpawanEnemy();
protected:
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
public:
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, Category = "Enemy Values")
USceneComponent* SceneComponent;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, Category = "Enemy Values")
UStaticMeshComponent* SpawanEnemyActor;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, Category = "TargetPoint")
UParticleSystemComponent* TargetSpawaning;
};
Game-play classes generally have separated and unique class header files. These classes files matched what type class of you defined, with A or U prefix and using .h file Extension. In top of file game-play class is Actor and uses AES_SpawanEnemy prefix; Class header files for game-play use standard c++ syntax in conjunction with specialized macros to simplify the process of declaring classes, variables and functions.You can see the generated header file( automatically generated) include needs to be include.
Class Declaration
Defines the name of the class, what class inherit from and any functions and variables it inherits.
UCLASS([specifier, specifier, ...], [meta(key=value, key=value, ...)])
class ClassName : public ParentName
{
GENERATED_BODY()
}
Standard C++ class declaration for the class. Described such as class specifiers and metadata are passed in UCLASS() macro, used for create UClass for the being declared, which can be thought of as the engine’s specialized representation of the class. GENERATED_BODY() must be placed at the very first of class body;
Class Specifiers
Abstract -> preventing the user from adding Actors of this class to level.
AdvancedClassDisplay -> forces all properties of the class to show only in advanced sections of any details panel where the appear;
AutoCollapseCategories=(Category1, Category2, …) -> Navigates the effects, for the listed categories of the AutoExpandCategories Specifier on a parent class.
AutoExpandCategories=(Category1, Category2, …) -> Specifiers one or more categories that should be automatically expanded in the unreal editor Property window.
Blueprintable -> Expose this class as an acceptable base class for creating Blueprints. Default is NotBlueprintable.
BlueprintType -> Expose this class as type that can be used for variables in Blueprints;
ClassGroup = GroupName -> Indicates that unreal Editor Actor Browser should include this class and any subclass of this class with Groupname. Group View is enabled in the Actor Browser.
CollapseCategories -> this class properties should not be grouped in categories in Unreal editor property window.
Config=ConfigName -> Allow that this class is allowed data in config file .ini.
Const -> All properties and function in this class are const and exported as const. This specifier is inherit by subclass.
More!!
Metadata Specifiers
Use : metadata specifiers differs between regular class, functions and interfaces.
BlueprintSpawnableComponent -> If present the Component class can be spawned by a Blueprint;
BlueprintThreadSafe -> Only valid blueprint function Lib. This specifier marks the functions in this class as callable on non-game threads in Animation Blueprints.
DisplayName=”Blueprint Node Name” -> The name of node in Blueprint will be replaced with the value;
ShortToolTip=”Short tooltip” -> short tool tip
More!!
Class Implementation
All game-play classes must use the GENERATED_BODY macro in order to be implemented properly.
The Source file [.cpp] must include Header File that contains the c plus declaration, and generated automatically.
Class Constructor
UObjects use Constructors to set default value for properties and other variables as well.
// Sets default values
AES_SpawanEnemy::AES_SpawanEnemy()
{}
Read from Official Docs